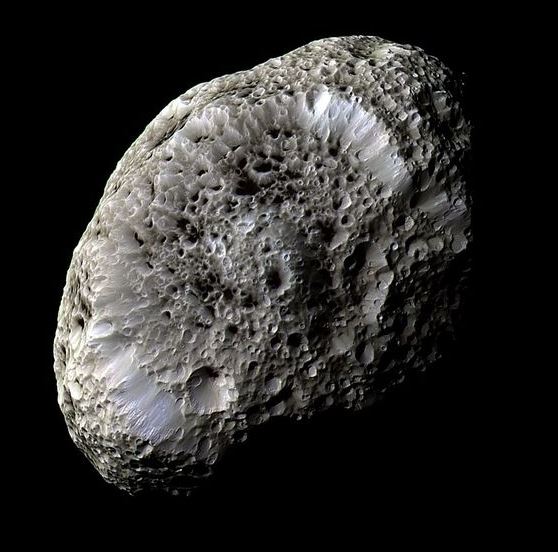
Adrastea is one of Jupiter’s intriguing moons, known for its small size and close proximity to the giant planet. As a member of Jupiter’s inner moon group, Adrastea orbits at a distance that places it near the planet’s rings. This positioning makes it part of a fascinating collection of small, irregularly shaped moons that circle Jupiter in tight orbits. Despite its modest size, Adrastea offers valuable insights into the composition and characteristics of small celestial bodies within our solar system.
1. Surface and Composition
Ice and Rock
Description of Composition: Adrastea’s surface is primarily composed of a blend of ice and rock. The moon’s low density indicates that ice is a significant component of its makeup. This combination is typical of small, irregular moons that often have a porous structure, allowing for a mix of these materials. The exact ratio of ice to rock on Adrastea remains uncertain, but its overall density supports the presence of a substantial icy component.
Comparison: When compared to other small, irregular moons of Jupiter, Adrastea’s composition is quite similar. Many of these moons, like Metis and Amalthea, also exhibit a mixture of ice and rock. This commonality suggests that the processes that formed and influenced these moons likely involved similar materials and conditions.
Density Implications: Adrastea’s low density, approximately 1.8 grams per cubic centimeter, reveals much about its internal structure. A lower density compared to typical rocky bodies indicates that the moon contains a considerable amount of ice. This low density is a key factor in understanding Adrastea’s composition, as it helps confirm the presence of significant icy components mixed with rock.
Regolith
Definition: Regolith refers to the layer of loose, fragmented material that covers the surface of a celestial body. It is a crucial element for understanding the surface composition of moons and planets, providing insights into the materials present and their distribution.
Composition of Regolith: On Adrastea, the regolith is composed of a mix of rocky and icy particles. This mixture contributes to the moon’s overall surface characteristics and density. The regolith on Adrastea likely includes fragments of both ice and rock, reflecting the moon’s complex formation history and its exposure to various space debris impacts.

2. Density and Size
Density
Measurement: Adrastea has a density of approximately 1.8 grams per cubic centimeter. This measurement is crucial for understanding the moon’s composition and internal structure.
Implications: The low density of Adrastea suggests a significant presence of water ice mixed with rock. In celestial bodies, density is a direct indicator of composition. A low density like Adrastea’s typically points to a higher proportion of ice relative to rock. Since ice is less dense than rock, the low overall density supports the idea that Adrastea contains a substantial amount of water ice.
Size
Diameter: Adrastea has a diameter of about 20 kilometers (12 miles). This relatively small size places it among the smaller moons in Jupiter’s system.
Impact on Density: The small size of Adrastea contributes to its low mass and, consequently, its low density. Smaller moons like Adrastea often have lower densities due to their reduced mass and volume, which can result in a more porous structure. The limited size means there is less gravitational force to compress the moon’s material, allowing it to retain a significant amount of ice, which further influences its overall density.

3. Surface Features
Cratering and Impact Evidence
Surface Characteristics: Adrastea’s surface is marked by numerous impact craters, a clear indication of collisions with space debris. These craters vary in size and depth, reflecting the moon’s exposure to meteorites and other small celestial objects over time. The presence of these craters suggests that Adrastea, despite its small size, has been subjected to significant space weathering and impacts.
Implications: The impact craters on Adrastea reveal several important aspects of the moon’s surface. First, they indicate that the surface is relatively weak and not very solid, which aligns with the low density and porous nature of the moon. The cratering also suggests that the surface material, a mixture of ice and rock, can easily be disrupted by collisions. This impact evidence provides insights into the moon’s surface composition and helps scientists understand its geological history.
Summary: Adrastea is a small moon of Jupiter characterized by its icy and rocky composition, low density, and notable surface features. Its surface is covered with impact craters, indicating a history of collisions and a relatively weak surface structure. The moon’s low density points to a significant amount of water ice mixed with rock, while its small size contributes to its overall mass and density.
Significance: Studying Adrastea and other similar moons is crucial for understanding the formation and evolution of celestial bodies in the solar system. Insights gained from these moons help scientists learn more about the conditions and materials present in the early solar system, offering valuable clues about planetary and moon formation processes.
FAQ
1. What is Adrastea?
Adrastea is one of Jupiter’s small inner moons. It is part of the group of moons that orbit very close to the planet. Despite its small size, Adrastea provides valuable insights into the composition and characteristics of celestial bodies near Jupiter.
2. What is the composition of Adrastea?
Adrastea’s surface is primarily composed of a mix of ice and rock. The moon’s low density suggests a significant amount of water ice mixed with rock. The surface also features a regolith, a layer of loose, fragmented material consisting of both rocky and icy particles.
3. How dense is Adrastea?
Adrastea has a density of approximately 1.8 grams per cubic centimeter. This low density indicates that the moon contains a substantial amount of ice compared to rock.
4. What is the diameter of Adrastea?
Adrastea has a diameter of about 20 kilometers (12 miles). Its small size contributes to its low mass and density.
5. What can the impact craters on Adrastea tell us?
The impact craters on Adrastea provide evidence of collisions with space debris. These craters suggest that the moon’s surface is relatively weak and porous. The cratering also offers clues about the moon’s surface composition and its exposure to impacts over time.
6. Why is studying Adrastea important?
Studying Adrastea helps scientists understand the formation and evolution of small celestial bodies in the solar system. Insights gained from Adrastea and similar moons contribute to our knowledge of planetary and moon formation processes, as well as the conditions in the early solar system.
7. How does Adrastea compare to other moons of Jupiter?
Adrastea’s composition and characteristics are similar to other small, irregular moons of Jupiter, such as Metis and Amalthea. These moons often have a mixture of ice and rock and share similar low-density features due to their small size and porous structure.
8. What are the main surface features of Adrastea?
Adrastea’s surface is marked by numerous impact craters, which reveal the moon’s exposure to collisions with space debris. These craters suggest that the moon’s surface is relatively weak and that the impact events have played a significant role in shaping its appearance.