Afghanistan, a landlocked country in South Asia, has a rich and complex history that spans thousands of years. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Central and South Asia has made it a focal point for various civilizations and empires. This article delves into the history of Afghanistan, highlighting key events, influential figures, and the country’s cultural evolution.
Ancient Afghanistan: Early Civilizations and Empires
Afghanistan’s history can be traced back to ancient times, when it was home to several significant civilizations.
- Indus Valley Civilization: One of the earliest known civilizations, the Indus Valley Civilization, had trade interactions with what is now Afghanistan. The region known as Bactria, in northern Afghanistan, was part of this extensive trade network around 2500-1500 BCE.
- Persian Empire: In the 6th century BCE, Afghanistan was part of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great. The Persian influence introduced new administrative practices and cultural exchanges that shaped the region’s development.
- Alexander the Great: In the 4th century BCE, Alexander the Great conquered Afghanistan as part of his campaign to build an empire stretching from Greece to India. His conquests led to the spread of Hellenistic culture in the region, particularly in the city of Alexandria Arachosia (modern-day Kandahar).
- Maurya Empire: After Alexander’s death, the region was absorbed into the Maurya Empire under Chandragupta Maurya in the 3rd century BCE. His rule facilitated the spread of Buddhism into Afghanistan, leaving a lasting impact on the region.
The Medieval Period: Dynasties and Cultural Flourishing
During the medieval period, Afghanistan witnessed the rise and fall of various dynasties and empires.
- Kushan Empire: The Kushan Empire (1st to 4th centuries CE) was a significant power in Afghanistan. The Kushans promoted trade along the Silk Road and played a crucial role in the spread of Buddhism across Central Asia.
- Ghaznavid Empire: In the 11th century, the Ghaznavid Empire, founded by Mahmud of Ghazni, established its dominance over Afghanistan. The Ghaznavids are noted for their patronage of the arts and sciences, as well as their military campaigns into India.
- Ghurid Empire: Following the decline of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid Empire (12th to 13th centuries) rose to prominence. The Ghurids, based in the region around modern-day Ghor, established a vast empire and left a legacy of architectural and cultural achievements.
- Mongol Invasions: The 13th century saw the Mongol invasions led by Genghis Khan and his successors. The Mongol invasions caused widespread devastation in Afghanistan but also facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between East and West.
The Early Modern Period: The Rise of Modern States
The early modern period was marked by the emergence of powerful states and the shaping of Afghanistan’s modern borders.
- Timurid Empire: In the 14th and 15th centuries, the Timurid Empire under Timur (Tamerlane) extended its influence into Afghanistan. The Timurids are known for their contributions to art, architecture, and science.
- Mughal Empire: In the 16th century, the Mughal Empire, which originated in India, extended its influence into Afghanistan. The Mughal rulers, including Babur and Akbar, had a significant impact on the region’s politics and culture.
- Safavid and Uzbek States: The Safavid Empire in Persia and the Uzbek states in Central Asia also vied for control over parts of Afghanistan during this period, contributing to the region’s complex political landscape.

The Modern Era: Colonialism, Independence, and Conflict
The 19th and 20th centuries were a time of significant change and conflict for Afghanistan.
- British and Russian Rivalry: During the 19th century, Afghanistan became a key battleground in the “Great Game” between the British Empire and the Russian Empire. The British sought to influence Afghanistan to secure their Indian Empire, while the Russians aimed to expand their territory.
- Anglo-Afghan Wars: Afghanistan experienced a series of conflicts with the British Empire known as the Anglo-Afghan Wars (1839-1842, 1878-1880, and 1919). The wars were marked by resistance from Afghan leaders and efforts to maintain sovereignty against British interference.
- Independence and Modernization: In 1919, Afghanistan gained full independence from British influence following the Third Anglo-Afghan War. The country embarked on a path of modernization under the leadership of King Amanullah Khan, who introduced various social and political reforms.
- Soviet Invasion: The late 20th century saw Afghanistan engulfed in conflict with the Soviet invasion of 1979. The Soviet intervention led to a decade-long war, marked by resistance from Afghan mujahideen fighters supported by the United States and other Western allies.
- Civil War and Taliban Era: After the Soviet withdrawal in 1989, Afghanistan descended into a civil war among various factions. In 1996, the Taliban, an extremist group, seized control and imposed a strict interpretation of Islamic law, leading to widespread human rights abuses.
- U.S. Invasion and Ongoing Conflict: In 2001, the U.S. led an invasion of Afghanistan following the September 11 attacks, aiming to dismantle al-Qaeda and remove the Taliban from power. The invasion led to a prolonged conflict involving international forces, Taliban insurgents, and ongoing challenges related to governance and security.
Contemporary Afghanistan: Challenges and Prospects
In recent years, Afghanistan has faced significant challenges, including political instability, economic difficulties, and ongoing conflict. However, the country also shows resilience and a desire for peace and development.
- Political Transition: Afghanistan has undergone several political transitions, including the establishment of a new democratic government and efforts to negotiate peace with the Taliban. The 2021 withdrawal of U.S. and NATO forces and the subsequent return of the Taliban to power have reshaped the country’s political landscape.
- Humanitarian Issues: The ongoing conflict has led to severe humanitarian crises, including displacement, poverty, and a lack of basic services. International organizations continue to provide aid and support for reconstruction and development efforts.
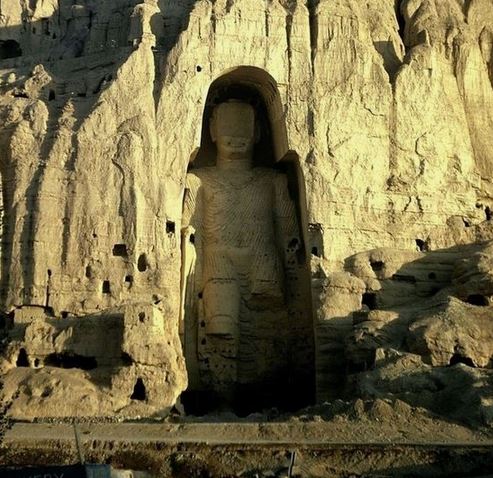
- Cultural Heritage: Despite the challenges, Afghanistan remains a country with a rich cultural heritage. Its historical sites, such as the ancient city of Bamiyan and the ruins of the Buddhist statues, are testaments to its historical significance and resilience.
The Legacy of Afghanistan
Afghanistan’s history is a testament to its strategic importance and the resilience of its people. From ancient civilizations and medieval empires to modern conflicts and reconstruction efforts, the country’s past is marked by both grandeur and adversity. Understanding Afghanistan’s history provides valuable insights into its current challenges and its enduring cultural and historical legacy. As the country moves forward, it continues to navigate the complexities of its past while striving for a more stable and prosperous future.