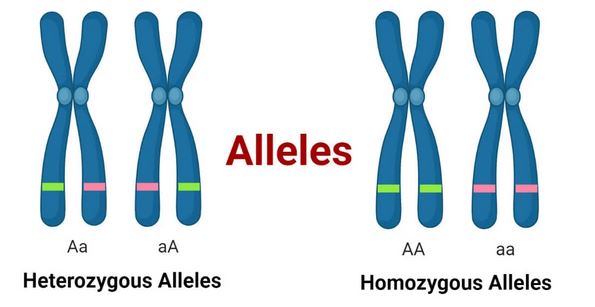
An allele is a variant form of a gene that can occupy the same position on a chromosome. Alleles are crucial in determining the genetic makeup of an organism and play a key role in the diversity of traits observed within a species. Understanding alleles helps explain how genetic traits are inherited and expressed in living organisms.
Understanding Alleles
- Genetic Variation: Alleles contribute to genetic variation by providing different versions of a gene. For instance, a gene that determines flower color in plants might have alleles for red, white, or yellow flowers.
- Homozygous and Heterozygous: An organism’s genotype refers to the combination of alleles it possesses for a specific gene. If an organism has two identical alleles for a gene, it is homozygous for that gene. If it has two different alleles, it is heterozygous.
- Dominant and Recessive Alleles: Alleles can be classified as dominant or recessive. A dominant allele masks the expression of a recessive allele when both are present. For example, if the allele for brown eyes is dominant and the allele for blue eyes is recessive, a person with one brown eye allele and one blue eye allele will have brown eyes.
Examples of Alleles
- Blood Type: The ABO blood group system is determined by three alleles: A, B, and O. The A and B alleles are dominant, while O is recessive. An individual’s blood type results from the combination of these alleles, such as AA, AO (for type A), BB, BO (for type B), AB (for type AB), and OO (for type O).
- Flower Color: In pea plants, the gene for flower color has two alleles: purple and white. The purple allele is dominant, so plants with either two purple alleles or one purple and one white allele will have purple flowers.
- Genetic Disorders: Some genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles. For example, cystic fibrosis is a condition caused by a recessive allele. An individual must inherit two copies of this recessive allele (one from each parent) to express the disorder.
The Role of Alleles in Evolution and Genetics
- Inheritance: Alleles are passed from parents to offspring through the process of reproduction. The combination of alleles inherited from each parent determines an organism’s genetic traits.
- Genetic Diversity: Alleles contribute to genetic diversity within a population. Variations in alleles can lead to different traits and adaptations, which are crucial for the survival and evolution of species.
- Population Genetics: The study of allele frequencies within populations helps scientists understand genetic diversity, evolution, and the impact of natural selection.
Alleles are fundamental components of genetics that determine the variation in traits among individuals. By influencing the expression of genes, alleles contribute to the rich diversity of life and play a central role in inheritance and evolution. Understanding alleles provides insight into how genetic traits are passed from one generation to the next and helps explain the variations observed in living organisms.