Approximants are a type of speech sound in phonetics characterized by a relatively open vocal tract, which allows for a smooth airflow without the complete closure that creates stops or the significant constriction found in fricatives. These sounds are crucial in language and linguistics for their role in producing various speech sounds.
Characteristics of Approximants
1. Articulatory Description
Approximants are produced with a constriction of the vocal tract that is narrower than for vowels but wider than for stops or fricatives. This constriction is not enough to cause turbulent airflow, which is why approximants do not produce the same type of noise as fricatives.
2. Types of Approximants
- Liquids: These include lateral approximants and rhotic approximants.
- Lateral Approximants: The airflow is directed around the sides of the tongue. An example is the English /l/ sound in “let.”
- Rhotic Approximants: The tongue is positioned in a way that causes some constriction but does not create a fricative sound. Examples include the American English /ɹ/ in “red” and the Scottish English /ɾ/ (flap) in “butter.”
- Glides: These are also known as semivowels and involve a slight constriction that is closer to that of vowels. Common glides include:
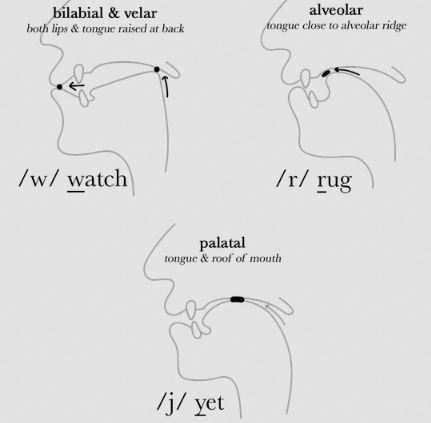
- /j/ as in “yes”
- /w/ as in “win”
Phonetic Notation and Classification
1. IPA Symbols
In the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), approximants are represented by specific symbols:
- /l/ for the lateral approximant
- /ɹ/ for the rhotic approximant
- /j/ for the palatal glide
- /w/ for the labial-velar glide
2. Place of Articulation
Approximants can be classified based on where in the vocal tract the constriction occurs:
- Labial: Involving the lips, as with /w/
- Palatal: Involving the middle of the tongue and the hard palate, as with /j/
- Velar: Involving the back of the tongue and the soft palate
Role in Phonology
1. Syllable Structure
Approximants often function as syllable nuclei or onsets in various languages. For instance, in English, approximants like /l/ and /w/ can appear at the beginning of syllables, affecting syllable structure and word formation.
2. Phonological Processes
Approximants play a role in phonological processes such as:
- Assimilation: Where approximants may influence the pronunciation of adjacent sounds.
- Elision: Where approximants can be dropped in rapid speech, affecting the fluidity of language.
Examples Across Languages
1. English
In English, approximants are common and occur frequently:
- /l/: Found in words like “light” and “love”
- /ɹ/: Found in words like “right” and “wrong”
- /j/: Found in words like “yellow” and “yes”
- /w/: Found in words like “win” and “wonder”
2. Other Languages
- Spanish: Uses approximants such as /ʎ/ (historically) and /ʃ/ in some dialects.
- French: Features the approximants /ʁ/ and /j/.
Approximants are essential components of phonetic systems in many languages. Their distinctive features—being articulated with a relatively open vocal tract—allow them to bridge the gap between vowels and other consonant types. Understanding approximants enhances our knowledge of how sounds are produced and utilized in language, contributing to the broader field of phonetics and phonology.