An Archimedean solid is a type of highly symmetrical polyhedron, composed of regular polygons that meet in the same pattern at each vertex. These polyhedra are named after the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes, who studied them extensively. Archimedean solids are distinct from Platonic solids because they allow for more than one type of regular polygon in their construction, though they still exhibit uniformity in their vertices.
There are 13 Archimedean solids, and they are important in geometry, architecture, and crystallography due to their symmetry and aesthetic appeal.
Characteristics of Archimedean Solids
Archimedean solids share the following characteristics:
- Convex Polyhedra: All Archimedean solids are convex, meaning no indentations in their surfaces.
- Regular Faces: Each face of an Archimedean solid is a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal), though different types of polygons can be present in the same solid.
- Vertex-Transitivity: The arrangement of polygons around each vertex is identical for all vertices of the polyhedron. This means that each vertex of an Archimedean solid looks exactly the same in terms of the surrounding polygons.
- Symmetry: They exhibit a high degree of symmetry, though not as much as Platonic solids, which are made up of only one type of polygon and are more symmetrical.
Difference Between Archimedean Solids and Platonic Solids
While both Archimedean and Platonic solids are highly symmetrical, the key differences are:
- Platonic solids are composed of only one type of regular polygon, while Archimedean solids can have two or more types of regular polygons.
- Platonic solids have identical faces and identical vertices, while Archimedean solids have identical vertices but not identical faces.
- There are only five Platonic solids, while there are thirteen Archimedean solids.
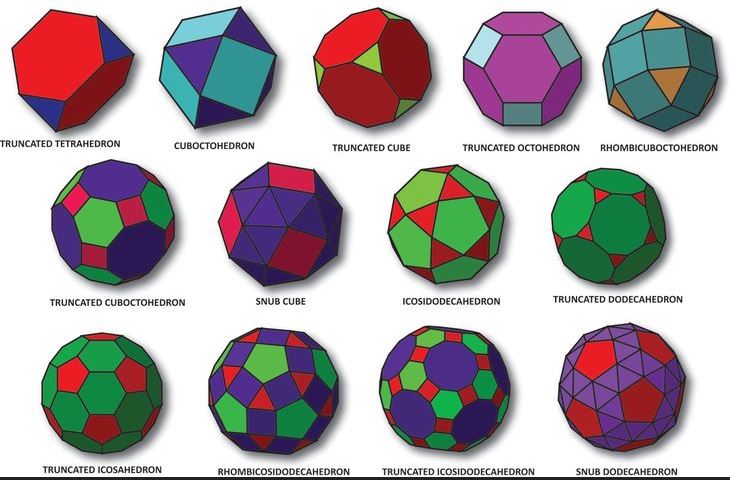
The 13 Archimedean Solids
The Archimedean solids are categorized based on the types of polygons that make up their faces and their symmetries. The 13 solids are as follows:
- Truncated Tetrahedron:
- Faces: 4 equilateral triangles and 4 regular hexagons.
- A truncated version of the tetrahedron.
- Cuboctahedron:
- Faces: 8 equilateral triangles and 6 squares.
- A polyhedron formed by combining features of a cube and an octahedron.
- Truncated Cube:
- Faces: 6 octagons and 8 equilateral triangles.
- Created by truncating (cutting off) the corners of a cube.
- Truncated Octahedron:
- Faces: 6 squares and 8 regular hexagons.
- A truncated version of an octahedron.
- Rhombicuboctahedron:
- Faces: 8 equilateral triangles and 18 squares.
- Related to the cube and octahedron, with square and triangular faces.
- Truncated Cuboctahedron (also called the truncated rhombicuboctahedron):
- Faces: 12 squares, 8 hexagons, and 6 octagons.
- A more complex truncation of the cuboctahedron.
- Snub Cube:
- Faces: 6 squares and 32 equilateral triangles.
- An asymmetrical version of the cube, rotated into a twisted shape.
- Icosidodecahedron:
- Faces: 12 regular pentagons and 20 equilateral triangles.
- A polyhedron combining features of the icosahedron and dodecahedron.
- Truncated Dodecahedron:
- Faces: 12 decagons and 20 equilateral triangles.
- Formed by truncating the dodecahedron.
- Truncated Icosahedron:
- Faces: 12 regular pentagons and 20 hexagons.
- This is the shape of a soccer ball and the carbon molecule C60 (buckyball).
- Rhombicosidodecahedron:
- Faces: 30 squares, 20 equilateral triangles, and 12 regular pentagons.
- Related to the icosahedron and dodecahedron.
- Truncated Icosidodecahedron (also called the truncated rhombicosidodecahedron):
- Faces: 30 squares, 20 hexagons, and 12 decagons.
- A complex truncation of the icosidodecahedron.
- Snub Dodecahedron:
- Faces: 12 regular pentagons and 80 equilateral triangles.
- A twisted version of the dodecahedron, with a more asymmetrical shape.
Construction and Geometry
Archimedean solids can be constructed by truncating or snubbing Platonic solids. For example:
- Truncation involves cutting off the vertices of a Platonic solid to form new faces. For instance, truncating a cube gives rise to the truncated cube, where the corners are replaced by equilateral triangles, and the original faces become octagons.
- Snubbing refers to twisting or rotating faces to create new configurations, as seen in the snub cube and snub dodecahedron.
Applications of Archimedean Solids
Archimedean solids are important in various scientific and practical applications due to their structural stability and symmetry:
- Chemistry: Some Archimedean solids, such as the truncated icosahedron, resemble the structure of molecules like fullerenes (C₆₀), which are carbon allotropes used in nanotechnology.
- Architecture: The geometries of Archimedean solids have been used in architectural designs and engineering structures due to their aesthetic symmetry and strength. Geodesic domes and polyhedral frameworks often draw from these shapes.
- Games and Art: Archimedean solids are used in dice design and art, as their symmetric forms appeal aesthetically and provide uniformity in game mechanics.
Archimedean solids represent a fascinating class of polyhedra that balance symmetry and diversity in their structures. While not as simple as Platonic solids, their combination of regular polygons and uniform vertices makes them essential in both theoretical geometry and practical applications. From molecular models to architectural wonders, Archimedean solids continue to inspire exploration and innovation in various fields.